Simulator¶
This page describes the class Simulator
The class Simulator is derived from SimParams and contains the actual simulation loop and handles events.
- Code:
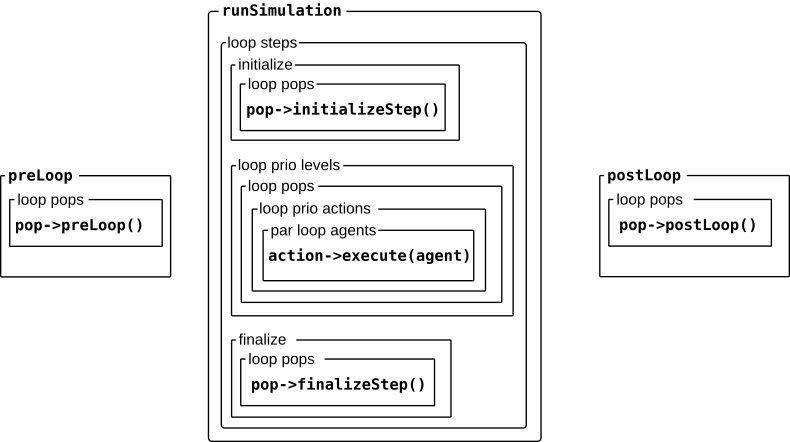
The processes of a simulation.¶
The above figure shows the entire sprocess of a simulation (cf Simulator::runSimulation()).
Before the simulation loop
In the preLoop stage all populations get to call their preLoop() methods which
in turn call the preLoop methods of all their actions.
Inside the simulation loop
The actual simulation loops through a predefined number of steps, or until all populations have died out.
In each step, all populations get to call their initializeStep() method which in turn calls the initialize() methods for each of their actions.
After this, a loop over all priority levels is started (here the lower priority levels come first), to ensure that the order of the actions is ensured.
For each priority level there is a loop over all populations, which calls all their actions pertaining to this priority level.
Each of these actions is then applied to each agent of the current population (in a parallelized loop).
As the lats phase of the simulation step, once all priority levels have been processed, a new loop over all populations is executed in which each population calls its finalizeStep() method (which in turn calls the finalize() method of each of its actions)
After the simulation loop
- After the main simulation loop has terminated, there is a final loop over all populations letting them call their
postLoop()methods, which calls alltheir actions’
postLoop()methods.
Public Methods¶
constructor¶
Simulator();
Some initialisation.
destructor¶
virtual ~Simulator();
The destructor deletes some objects that have been created.
isReady¶
bool isReady();
Returns true if everything is ok for the simulation to start (a valid cell grid exists and there is at least one non-empty population)
runSimulation¶
int runSimulation();
This method runs the simulation. It calls preLoop(), runLoop() and postLoop().
writeState¶
int writeState(const std::string sQDFOut, int iWhat, std::vector<std::pair<std::string, int>> &vSub, int iDumpMode);
sQDFOutName of output file.
iWhatAn or-ed combination of output flags determining what to write to file-
Name |
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
output_flag::WR_NONE |
0 |
Write nothing |
output_flag::WR_GRID |
1 |
Write the grid data |
output_flag::WR_GEO |
2 |
Write the geography data |
output_flag::WR_CLI |
4 |
Write the climate data |
output_flag::WR_VEG |
8 |
Write the vegetation data |
output_flag::WR_NAV |
16 |
Write the navigation data |
output_flag::WR_ALL |
31 |
Write all environment data |
output_flag::WR_MOV |
32 |
Write move statistics |
output_flag::WR_OCC |
64 |
Write occupation data |
output_flag::WR_POP |
128 |
Write population data |
vSubA vector of pairs of population names and an or-ed combination of
popwrite_flags. The populations named in this vector will be written to the output file.
Pop-specific Flag |
Value |
meaninging |
|---|---|---|
popwrite_flags::PW_NONE |
0 |
Write nothing |
popwrite_flags::PW_AGENTS_ONLY |
1 |
Write agent data only |
popwrite_flags::PW_STATS_ONLY |
2 |
Write move statistics only |
popwrite_flags::PW_ADDITIONAL_ONLY |
4 |
Write additional data only |
popwrite_flags::PW_ALL |
7 |
Write all |
iDumpModeDump mode
This method is called to write environment and/or population data to a QDF file.
showInput¶
void showInputs();
Displays the environment and population groups used in this simulation.
setInterrupt¶
void setInterrupt();
After this method is called, QHG will try to terminate gracefully when interrupted.