The QHG4 simulation framework: an Overview¶
QHG4 is a framework for agent-based simulations, together with a set of various tools.
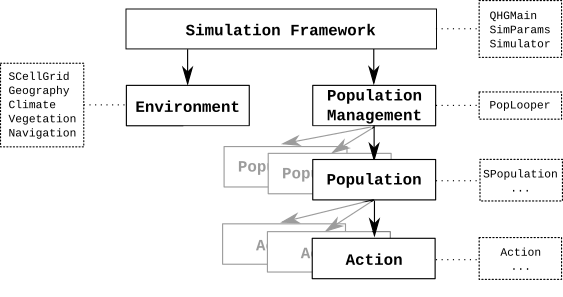
The arrows between the components (solid border) denote ownership, the boxes with dashed borders list the main classes associated with a component, with ‘…’ denoting derived classes.¶
Because the QHG code is parallized by means of OpenMP, the simulations run quite fast, on the order of less than 1 second for a single time step with a million agents.
- Short descriptions of the main elements
Simulation Framework¶
The simulation framework owns environment data as well as a population manager. During the simulation loop all agents in all populations will execute their actions. Additionally, events may change the environment or cause the output of population and/or environment data.
The essential classes for the simulation framework:
- QHGMain
opens the log file, creates a
Simulatorobject and runs it
- SimParams
base class for
Simulatorwith methods for reading program options, creating objects and loading data
- Simulator
runs the simulation loop and handles events
The description of the relevant classes can be found in the the “app” section of the documentation
Environment¶
- The essential environment classes:
- SCellGrid
The class SCellGrid implements the grid on which the simulation is running: agents sit on nodes and can travel to connected nodes. For global simulations the cellgrid is a subdivided Icosahedron, but planar grids with 4 or 6 neighborhood are also used.
- Geography
The class Geography contains longitudes, latitudes and altitudes of the nodes, as well as the water-related and glacial data
- Climate
The class Climate contains temperatures and precipitation for each cell
- Vegetation
The class Vegetation contains net primary production for each cell
- Navigation
The class Navigation contains over-seas connections for some nodes. This is used to allow agents to move to islands.
For input and output QHG uses files in the QDF file format to hold environment data.
Populations and Population Management¶
In QHG4 agents small structures containing the individuals’ properties. They are managed in population objects. Each population object has a parallelized loop to execute the actions of all its agents, and manages their birth, death and movement.
- PopLooper
Manages any number of
SPopulationobjects and distributes commands fromSimulatorto all of them.
- SPopulation
Base class for all population classes; only derived classes can be used as actual populations. Populations can use one or more
Actionobjects.
Actions¶
The actions agents perform during a simulation step are represented by classes derived from the base class Action.
There are actions for movement, mating, fertility, mortality, genetics and more.
See AgentManagement for more information.
Events¶
In order to trigger specific actions, mainly reading and writing data, QHG4 uses so-called events. Usually a list of times (when to do something), event types (what to do), and arguments (what to do it to) are passed to QHG4 as parameters. During execution, whenever the current simulation time matches a time on the event list, the actions for corresponding event(s) are executed.